Pyqt New Style Signals And Slots
| Trolltech Documentation Qt Quarterly « ImplementingModel/View/Controller Scripting Qt » |
PyQt5 - Signals & Slots Unlike a console mode application, which is executed in a sequential manner, a GUI based application is event driven. Functions or methods are executed in response to user’s actions like clicking on a button, selecting an item from a collection or a mouse click etc., called events. PyQt is more versatile than C/Qt in this regard, because we can connect not just to slots, but also to any callable, and from PyQt 4.2, it is possible to dynamically add 'predefined' signals and slots to QObjects. Let's see how signals and slots works in practice with the Signals and Slots program shown in Figure 4.6. PyQt5 signals and slots Graphical applications (GUI) are event-driven, unlike console or terminal applications. A users action like clicks a button or selecting an item in a list is called an event. If an event takes place, each PyQt5 widget can emit a signal. This section describes the new style of connecting signals and slots introduced in PyQt4 v4.5. One of the key features of Qt is its use of signals and slots to communicate Their use encourages the development of reusable components.
| Mapping Many Signals to One |
| by Jasmin Blanchette |
Qt allows us to connect multiple signals to the samesignal or slot. This can be useful when weprovide the user with many ways of performing the same operation.Sometimes, however, we would like the slot to behave slightlydifferently depending on which widget invoked it. In this article weexplore various solutions, including the use of QSignalMapper.
To illustrate the problem, we will implement a Keypad widget thatprovides ten QPushButtons, numbered 0 to 9, and adigitClicked(int) signal that is emitted when the user clicks abutton. We will review four solutions and discuss their respectivemerits.
The most straightforward solution to our problem (but also thesilliest) is to connect the ten QPushButton objects'clicked() signals to ten distinct slots calledbutton0Clicked() to button9Clicked(), each of which emits thedigitClicked(int) signal with a different parameter value (0 to9). Here's the definition of the Keypad class:
This is the Keypad constructor:
In the constructor, we create the QPushButtons, and we tediouslyconnect each button's clicked() signal to the correspondingprivate slot.
Each slot simply emits the digitClicked(int) signal with adifferent hard-coded argument.
Needless to say, this approach is inflexible and error-prone. It ispracticable for a small number of connections, but even for a10-key Keypad, the copy/paste is almost unbearable. Let's moveon to a better solution.
The next step is to merge thebuttonNClicked() slots into one private slotthat emits the digitClicked(int) signal with the correctparameter, depending on which button was clicked. This is possibleusing the QObject::sender() function, aswe will see shortly. The Keypad constructor becomes:
And this is the code for the buttonClicked() slot:
We start by calling sender() to retrieve a pointer to the QObjectthat emitted the signal that invoked this slot. In this particularexample, we know that the sender is a QPushButton, so we can castsender()'s return value to a QPushButton*. Then we emitthe digitClicked(int) signal with the digit value shown on thebutton.
The drawback of this approach is that we need a private slot to dothe demultiplexing. The code in buttonClicked() isn't veryelegant; if you suddenly replace the QPushButtons with anothertype of widget and forget to change the cast, you will get a crash.Similarly, if you change the text on the buttons (for example, 'NIL'instead of '0'), the digitClicked(int) signal will be emittedwith an incorrect value.
Finally, the use of sender() leads to tightly coupled components,which many people consider to be bad programming style. It isn't quiteso bad in this example, because Keypad already knows about thebutton objects, but if buttonClicked() was a slot in anotherclass, the use of sender() would have the unfortunate effect oftying that class to an implementation detail of the Keypad class.
Our third approach requires no private slot in Keypad; instead,we make sure that the buttons themselves emit a clicked(int)signal that can be directly connected to Keypad'sdigitClicked(int) signal. (When connecting a signal to anothersignal, the target signal is emitted whenever the first signal isemitted.) This requires subclassing QPushButton as follows:
Whenever QPushButton emits the clicked() signal, we interceptit in our KeypadButton subclass and emit the clicked(int)signal with the correct digit as the argument.
The Keypad constructor then looks like this:
This approach is both flexible and clean, but it is quite cumbersometo write, because it forces us to subclass QPushButton.
The fourth and last approach does not require any private slots,nor does it need a QPushButton subclass. Instead, the entiresignal-related logic is implemented in the Keypad class'sconstructor:
First, we create a QSignalMapper object. QSignalMapperinherits from QObject and provides a means of establishing arelationship between a set of zero-parameter signals and aone-parameter signal or slot. The call to setMapping() inside thefor loop establishes a mapping between a button and an integervalue; for example, buttons[3] is associated with the integervalue 3.
When the clicked() signal of a button is emitted,QSignalMapper's map() slot is invoked (thanks to theconnect() call in the for loop). If a mapping exists for theobject that emitted the signal, the mapped(int) signal is emittedwith the integer value set using setMapping(). That signal is inturn connected to the Keypad's digitClicked(int) signal.The setMapping() function exists in two versions: one that takesan int and one that takes a QString as the second argument.This makes it possible to associate an arbitrary string with a senderobject, instead of an integer. When such a mapping exists,QSignalMapper emits a mapped(const QString &) signal.
QSignalMapper does not directly support any other data types. Thismeans that, for example, if you were to implement a palette toolallowing the user to choose a color from a set of standard colors andneeded to emit a colorSelected(const QColor &) signal, your bestbet would be to use the sender() approach or the subclass approachdescribed above. If you already use a subclass of, say,QToolButton to represent a color, it doesn't cost you much to adda clicked(const QColor &) slot to it.
Pyqt4 Signal Slot
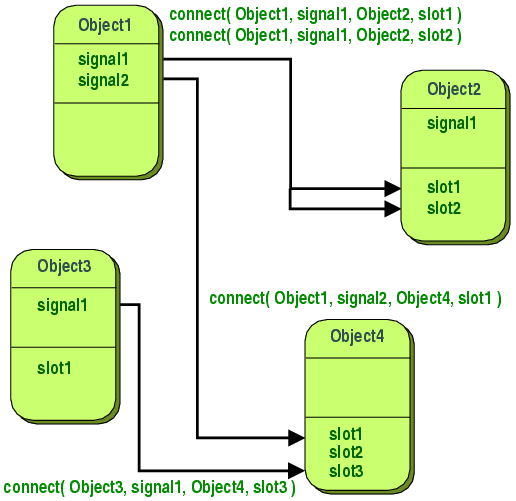
Signals And Slots Pyqt5
| Copyright © 2004 Trolltech | Trademarks | Scripting Qt » |